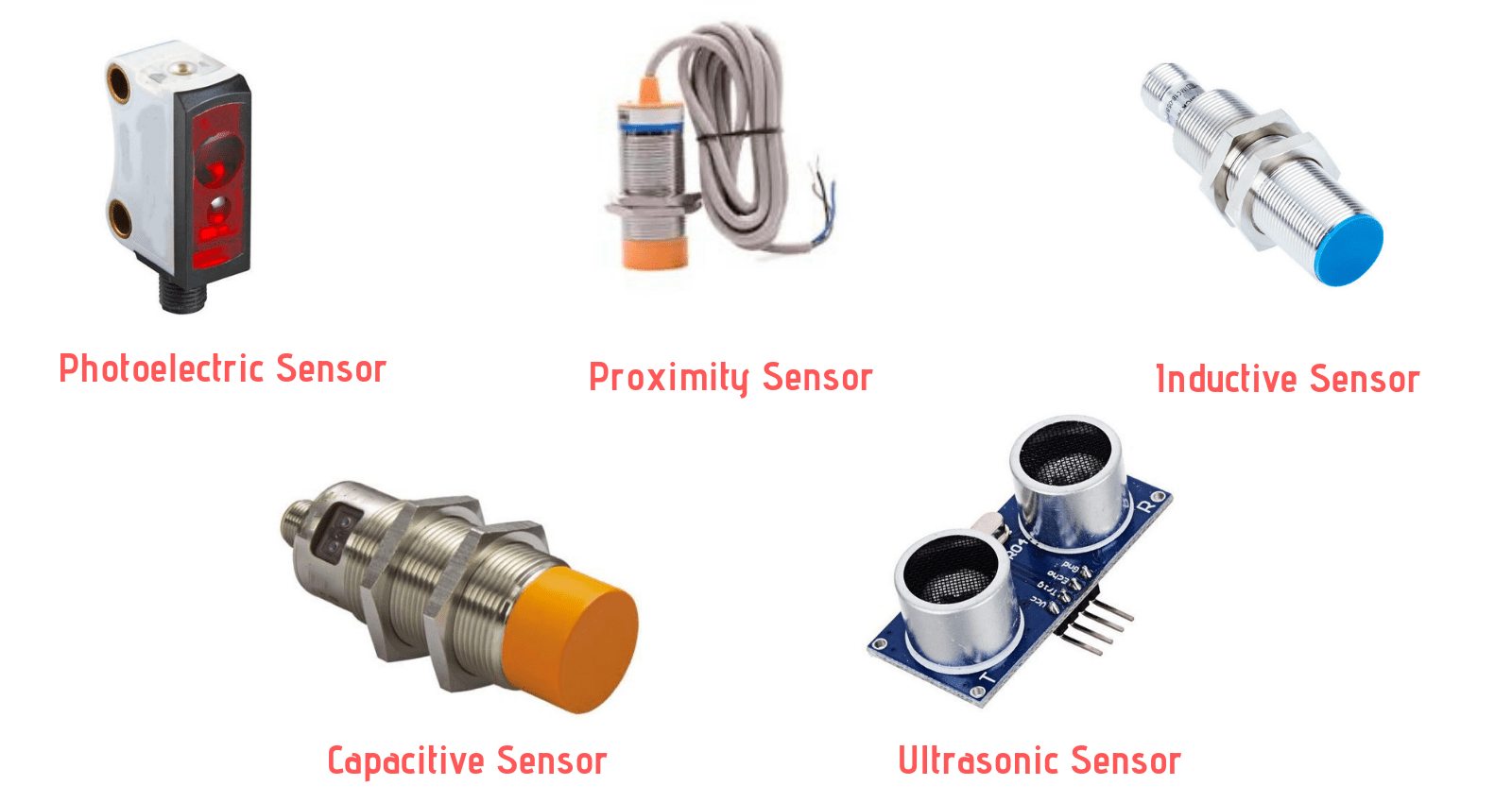
Proximity and ultrasonic sensors detect objects or distances without requiring physical contact. Proximity sensors work by emitting electromagnetic fields or using light radiation to identify changes in the nearby environment. They are widely employed in industrial machinery, mobile phones, and car parking systems to detect presence, position, or movement.
On the other hand, ultrasonic sensors operate by emitting ultrasonic waves and measuring the time taken for these waves to bounce back, indicating the distance to an object. They find extensive applications in automotive industries for parking assistance, water level measurement, and robotics for obstacle avoidance.
Both sensor types are crucial for enhancing efficiency and safety and facilitating automation across various domains, marking their significance in industrial and everyday applications.
In this article
Core Working Principles
Proximity Sensors Operation:
Proximity sensors detect objects without physical contact through electromagnetic fields or optical radiation. There are different types of proximity sensors, including inductive, capacitive, and photoelectric sensors.
- Inductive Proximity Sensors: Detect metallic objects by generating an electromagnetic field.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors: Identify materials based on their dielectric properties by detecting changes in capacitance.
- Photoelectric Proximity Sensors: Use light beams, detecting objects when they interrupt or reflect the light.
Ultrasonic Sensors Operation:
Ultrasonic sensors measure distance by emitting ultrasonic waves and receiving the echoes reflected from objects. The time interval between sending and receiving the lock is used to determine the length of the thing using the speed of sound formula. This method allows ultrasonic sensors to provide accurate distance measurements, making them suitable for various applications,, including obstacle detection and fluid level measurement.
Key Functional Differences
Understanding the functional differences between Proximity Sensors and Ultrasonic Sensors is essential for choosing the right sensor for a particular application. Here are the main differences concerning sensing range, material detection capabilities, and environmental resistance:
| Feature | Proximity Sensors | Ultrasonic Sensors |
| Sensing Range | Typically shorter (up to a few centimeters) | Longer (up to several meters) |
| Material Detection | – Metals (inductive) <br>- Any material (capacitive and photoelectric) | Almost any material, as long as it can reflect sound waves |
| Environmental Resistance | Varies; may be affected by electromagnetic interference or materials in the environment | Less affected by environmental factors, but performance may degrade with temperature extremes or high humidity |
Sensing Range:
Proximity Sensors generally have a shorter sensing range, usually up to a few centimeters. On the contrary, Ultrasonic Sensors can detect objects up to several meters away, making them more suitable for applications requiring longer-range detection.
Material Detection Capabilities:
Proximity Sensors have varied material detection capabilities. Inductive types are limited to detecting metallic objects, while capacitive and photoelectric types can see almost any material. Ultrasonic Sensors, however, can detect nearly any material, provided it can reflect sound waves.
Environmental Resistance:
The performance of Proximity Sensors may be affected by electromagnetic interference or the materials present in the environment. Environmental factors less impact Ultrasonic Sensors but may see degraded performance with temperature extremes or high humidity levels.
Application Domains: Where They Excel
Understanding the domains where these sensors excel will help you select the right sensor for your project or application.
Common Applications of Proximity Sensors:
- Industrial Automation:
- Monitoring the presence or absence of objects on a production line.
- Detecting the position of machine components for safety and operational efficiency.
- Vehicle Systems:
- Parking sensors to aid drivers in detecting obstacles while parking.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Seeing whether a smartphone is held near the ear to turn off the display.
- Security Systems:
- Intruder detection in security alarm systems.
Common Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors:
- Distance Measurement:
- Measuring the distance or level of liquids in tanks.
- Monitoring the height of items on a conveyor belt.
- Automotive Industry:
- Parking assistance systems to help drivers detect obstacles.
- Robotics:
- Obstacle detection and avoidance in autonomous robots.
- Medical Devices:
- Fluid level detection in medical equipment.
Each type of sensor has its own set of applications where it tends to excel. While proximity sensors are excellent for detecting the presence or absence of objects nearby, ultrasonic sensors provide valuable distance measurement capabilities in various fields.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of both Proximity Sensors and Ultrasonic Sensors can help make an informed decision based on the specific needs of your application.
| Feature | Proximity Sensors | Ultrasonic Sensors |
| Advantages | ||
| Sensing Range | Suitable for short-range detection | Capable of long-range detection |
| Material Detection | Can detect metallic (inductive) and any material (capacitive, photoelectric) | Can detect almost any material as long as it reflects sound waves |
| Installation Simplicity | Generally easy to install and configure | Also easy to install and configure |
| Cost | Often more cost-effective | May be more expensive |
| Disadvantages | ||
| Sensing Range | Limited to short-range detection | May not work well for close-range detection |
| Environmental Interference | May be affected by electromagnetic interference | Less affected by environmental conditions but performance may degrade with temperature extremes or high humidity |
| Material Limitation | Highly accurate in detecting the presence | No material limitation but surface should reflect sound waves |
| Accuracy | No material limitation but the surface should reflect sound waves | Accurate in distance measurement, may have issues with soft, uneven, or angled surfaces |
Cost Implication: An Overview
The pricing of sensors is a crucial factor to consider based on the budget and requirements of your project.
Proximity Sensors:
Proximity sensors are often more cost-effective, with prices ranging from around $10 to over $100 based on the type, brand, and specifications.
Ultrasonic Sensors:
Ultrasonic sensors typically have a higher price point due to their long-range sensing capabilities, ranging from around $20 to over $200.
The cost variation between these two types of sensors reflects their differing capabilities and the technologies employed within them. Making an informed choice based on budget and functional requirements is crucial for achieving desired outcomes in your applications.
Selecting the Right Sensor for Your Needs
Choosing the right sensor hinges on the specific requirements of your project. Here are some factors to consider:
- Sensing Range: Determine the required sensing range – proximity for short-range, ultrasonic for longer range.
- Material Detection: If material detection is vital, consider the type of materials you need to detect.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental conditions where the sensor will operate.
- Cost: Align your budget with the sensor that meets your functional needs.
- Ease of Installation and Configuration: Evaluate the ease of installation and technical support available.
Real-world Case Studies
Proximity Sensors:
- Automated Assembly Lines: Employed to ensure parts are properly aligned before moving to the next station.
- Vehicle Parking Assistance: Helps drivers detect nearby obstacles when parking.
Ultrasonic Sensors:
- Liquid Level Measurement: Used in water treatment plants to monitor water levels.
- Robotics: Employed in robots for obstacle detection and navigation.
Closing Thoughts
The comparison between Proximity and Ultrasonic Sensors sheds light on their distinct functionalities and application domains. While proximity sensors excel in detecting the presence or absence of objects in close range, ultrasonic sensors provide valuable distance measurement capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the core operational principles and functional differences is crucial.
- Assessing the application domains and real-world case studies aids in making an informed decision.
- Aligning the cost and specific project requirements helps in selecting the right sensor.
Should you require further assistance in choosing the right sensor for your project or have any product inquiries, please reach out. Our team is here to assist you in making an informed decision to ensure the success of your endeavors.